Treatment For Afib In Elderly
Treatment for afib in elderly. A final treatment called the Maze procedure may be used to treat AFib when medications and other procedures have failed. Old age alone should never be viewed as a contraindication for warfarin. Without treatment symptoms may get worse.
This downloadable sheet Partnering in Your Treatment PDF can help you discuss your goals and options with your healthcare provider. To determine the best therapeutic approach the risk of stroke and bleeding should be assessed in every patient and also periodically analysed. That said a good understanding of A-ib and keeping a close eye on an elder patient with the condition can keep the disease regulated.
It may be possible for you to be treated by a GP or you may be referred to a heart specialist a cardiologist. Treatment of AF should include treatment of the underlying disease such as hyperthyroidism pneumonia or pulmonary embolism when possible. But symptoms like a pounding or skipping heartbeat chest pain or dizziness can happen and are often related to a reduction in the amount of blood the heart pumps out.
To better prevent atrial fibrillation complications its important that you maintain a healthy weight lose weight if you are overweight exercise regularly manage high blood pressure and. In addition to knowing your goals you will want to discuss your treatment options and take an active role in your plan. Many of the oldest old are treated with aspirin instread of warfarin.
Another serious challenge in the management of chronic atrial fibrillation in older individuals is the prevention of stroke its primary outcome by choosing an appropriate antithrombotic treatment aspirin or. In this issue of JAHA Patti et al 12 provide evidence favoring treatment with anticoagulant therapy to prevent stroke or systemic embolism in the very elderly that outweighs the. Heart flutter or Afib even when being treated can and often does return and it tends to worsen over time as well.
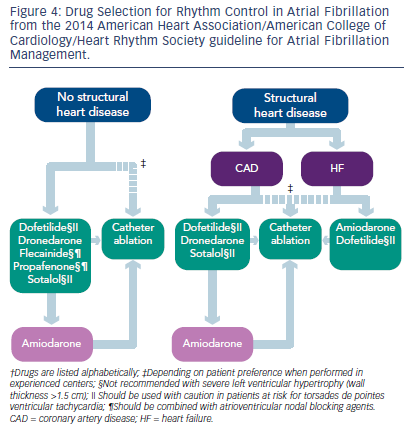
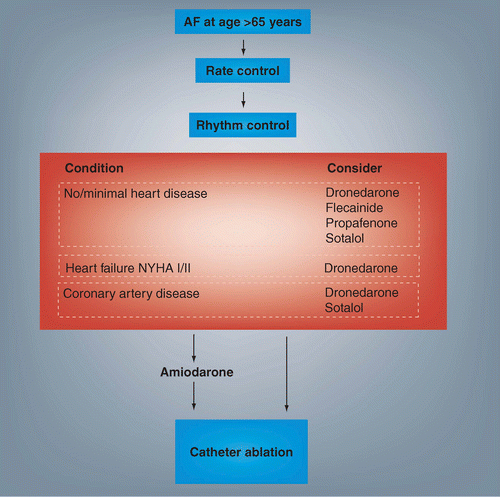
The great majority of elderly patients with AF should receive anticoagulant therapy unless there is an unequivocal contraindication. 8 According to current guidelines AF can be classified into different patterns depending on diagnosis duration termination and the strategy adopted by patient and physician rhythm or rate control. Aspirin does somewhat reduce stroke risk but not nearly as much as warfarin.
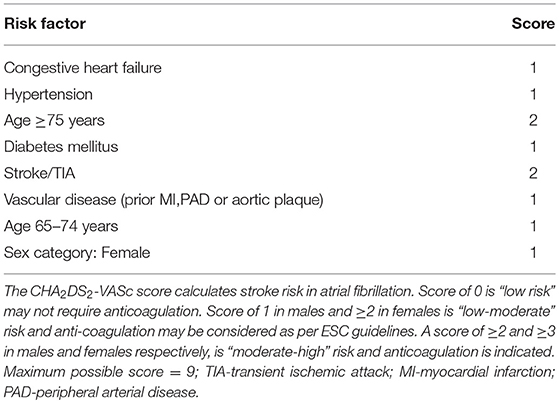
Both CHADS2 and the newer CHA2DS2-VASc scores1516emphasize the importance of increased age in the evaluation of thromboembolic risk. Doctors used to prescribe medication first for AFib.
Many of the oldest old are treated with aspirin instread of warfarin.
Old age alone should never be viewed as a contraindication for warfarin. Usually this is sufficient to control the symptoms in symptomatic patients and it is also the treatment choice in asymptomatic patients. Treatments for atrial fibrillation include medicines to control heart rate and reduce the risk of stroke and procedures to restore normal heart rhythm. Another serious challenge in the management of chronic atrial fibrillation in older individuals is the prevention of stroke its primary outcome by choosing an appropriate antithrombotic treatment aspirin or. To determine the best therapeutic approach the risk of stroke and bleeding should be assessed in every patient and also periodically analysed. Old age alone should never be viewed as a contraindication for warfarin. Heart flutter or Afib even when being treated can and often does return and it tends to worsen over time as well. Many patients in their 90s are safely managed with warfarin. So can ablation a treatment that creates scar tissue on your heart.
This downloadable sheet Partnering in Your Treatment PDF can help you discuss your goals and options with your healthcare provider. Elderly patients are especially vulnerable to stroke in the presence of AF thus they are more likely to benefit from oral anticoagulant therapy. Usually this is sufficient to control the symptoms in symptomatic patients and it is also the treatment choice in asymptomatic patients. Without treatment symptoms may get worse. Aspirin does somewhat reduce stroke risk but not nearly as much as warfarin. That said a good understanding of A-ib and keeping a close eye on an elder patient with the condition can keep the disease regulated. Old age alone should never be viewed as a contraindication for warfarin.







































Post a Comment for "Treatment For Afib In Elderly"