Legg Calve Perthes Disease Treatment In Adults
Legg calve perthes disease treatment in adults. These drugs slow or stop the natural process of bone loss preventing the loss of bone mass and preserving increased bone density and strength. Studies into the pathogenesis of femoral head deformity in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease LCPD have led to the consideration of bisphosphonates as a potential therapeutic adjunctive therapy. This disease typically occurs in males between 5 and 7 years of age and is bilateral in 1020 of patients 1.
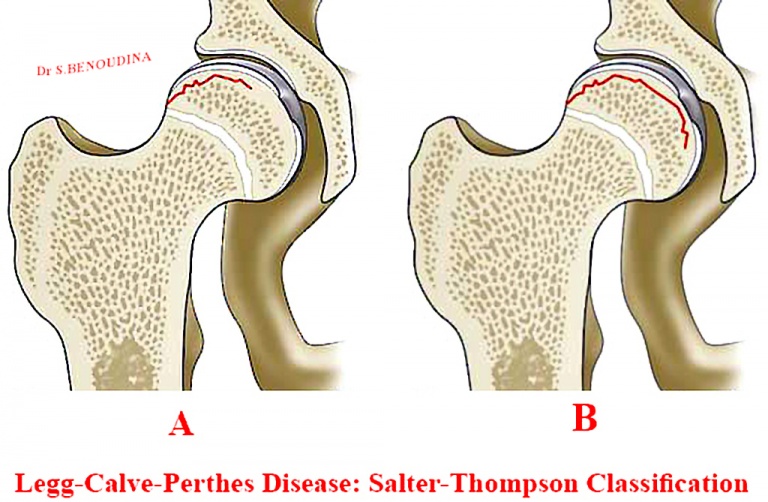
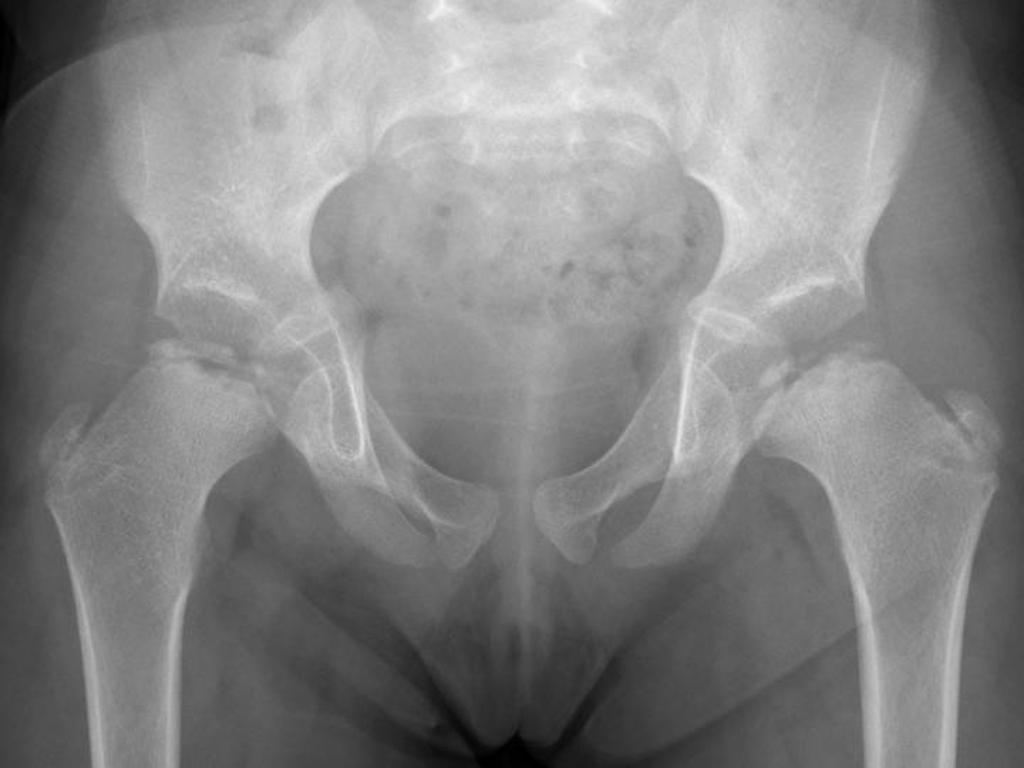
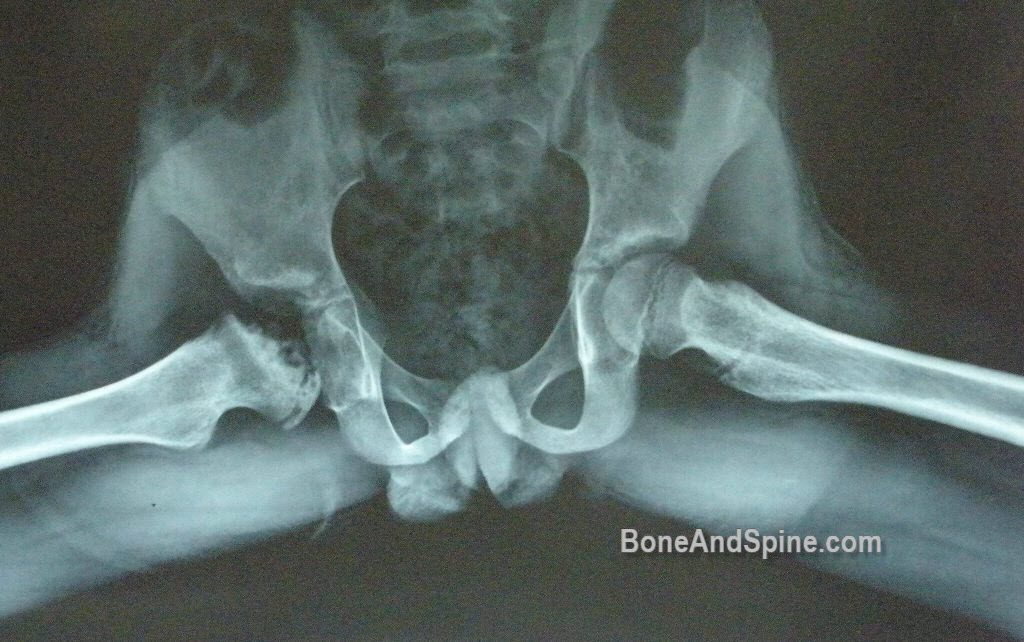
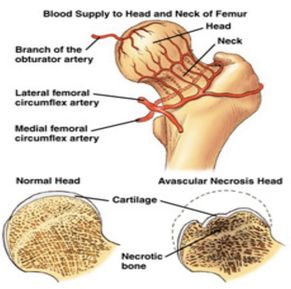
As necrosis spreads the ball develops a fracture of the supporting bone. In most patients pain resolves during the teenage years. However it is estimated that approximately 50 percent of patients who develop Legg-Calve-Perthes disease as a child will need a hip replacement by later adulthood ie 50 to 60 years old For more information you can visit the Perthes Association website.
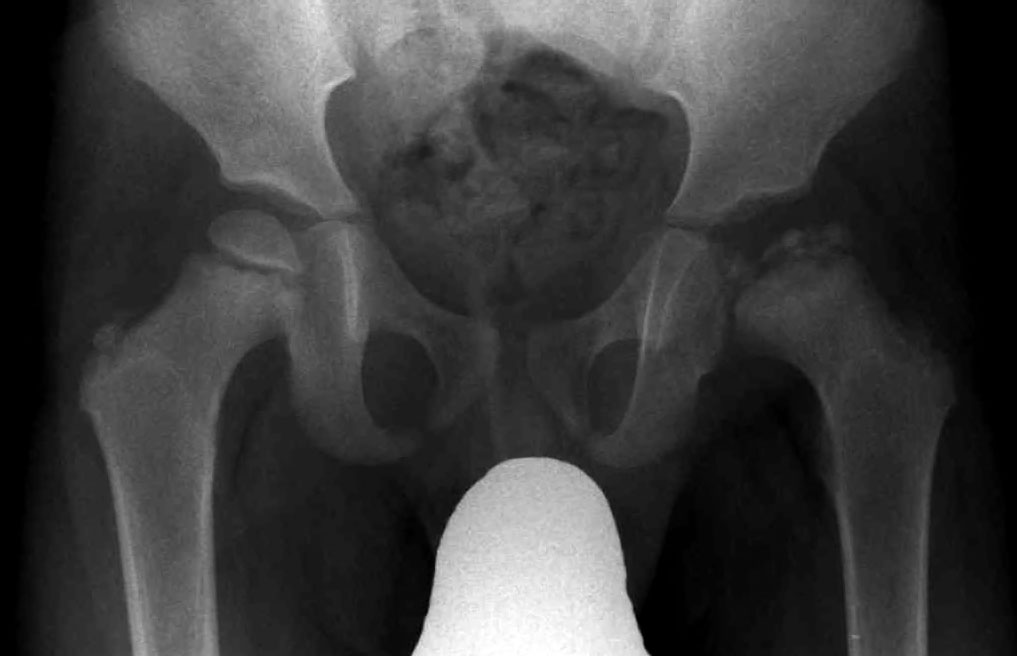
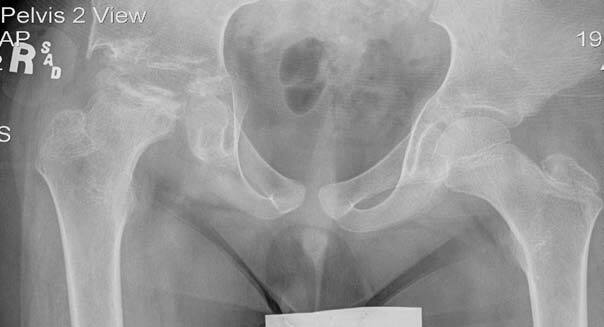
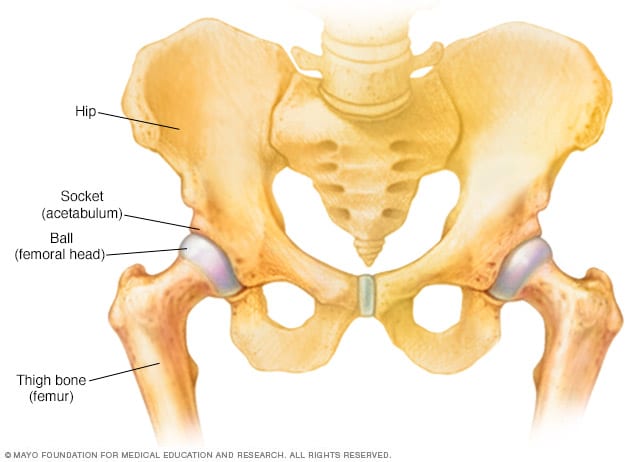
With Perthes blood flow to the ball of the hip is stopped and bone death necrosis occurs. One patient had a subsequent staged periacetabular osteotomy to improve acetabular coverage. Pain killer medications are prescribed.
Surgical containment is constant does not require an endpoint for discontinuing treatment and has a short treatment period. Patients without excessive lateral extrusion. The long-term natural history of LCPD is not known.
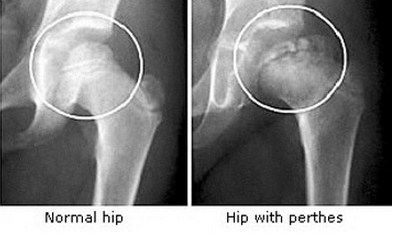
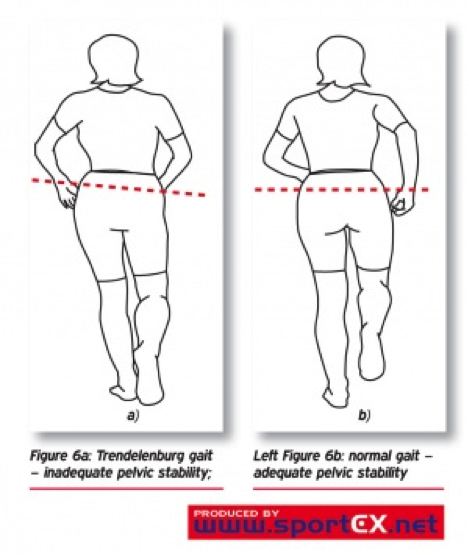
Legg-Calve-Perthes Syndrome is a degenerative hip joint disease that involves the loss of bone mass. Surgery to get taller also known as limb-lengthening surgery involves using surgical approaches to stimulate bone growth in the legs. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease Perthes is a rare disease that most often affects boys between the ages of 2 and 12.
Girls can have LPD. There has been some investigation into use a class of drugs known as bisphosphonates to treat individuals with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. The hips are the main problem.
Patient is advised to reduce his activities. Researchers performed a retrospective single-center review of.
However it is important to maintain mobility so that the joint does not become stiff.
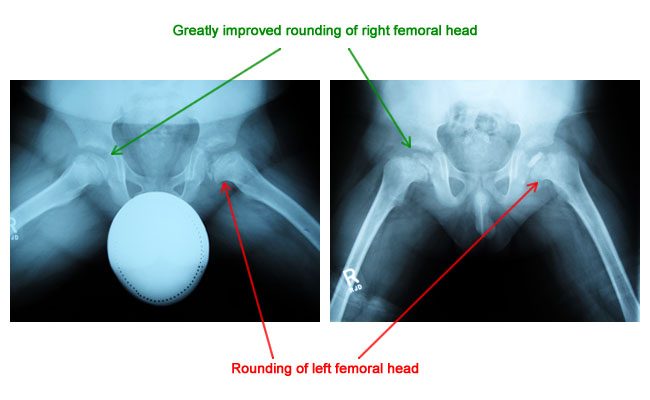
Patient is advised to reduce his activities. One patient had a subsequent staged periacetabular osteotomy to improve acetabular coverage. For patients with osteoarthritis associated with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease total hip arthroplasty provided excellent improvements in patient-reported outcomes and an acceptable complication rate according to published results. Between January 2003 and January 2009 14 patients with Perthes disease 4 female and 10 male patients with an average age of 196 years range 14 to 28 y were treated with SDO and trochanteric advancement. The mainstay treatment of legg calve perthes disease in adults is to alleviate symptoms and facilitate easy movement. In the literature long-term prognosis of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease LCPD means prognosis for secondary osteoarthritis of the hip joint or leg-length inequality and its consequences. With Perthes blood flow to the ball of the hip is stopped and bone death necrosis occurs. Although the cause of LCPD remains unknown the pathogenesis of the response to the avascular insult is becoming better understood. Surgery to get taller also known as limb-lengthening surgery involves using surgical approaches to stimulate bone growth in the legs.
One patient had a subsequent staged periacetabular osteotomy to improve acetabular coverage. Surgical containment is constant does not require an endpoint for discontinuing treatment and has a short treatment period. Patient is advised to reduce his activities. Although the cause of LCPD remains unknown the pathogenesis of the response to the avascular insult is becoming better understood. With Perthes blood flow to the ball of the hip is stopped and bone death necrosis occurs. These drugs slow or stop the natural process of bone loss preventing the loss of bone mass and preserving increased bone density and strength. The hips are the main problem.


/perthes-disease-4174322_FINAL-5c05c1c546e0fb0001f4a111.png)





























Post a Comment for "Legg Calve Perthes Disease Treatment In Adults"