Ground Glass Nodule Treatment
Ground glass nodule treatment. If a nodule has not increased in size over a series of scans or x-rays you will be informed that no more follow up is required. Doctors may use supplemental oxygen anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressant drugs. Surgical Resection for Ground Glass Opacity in Lungs Lobectomy with dissection of the mediastinal lymph nodes and ipsilateral hilar is the standard treatment option for non-small cell lung cancer.
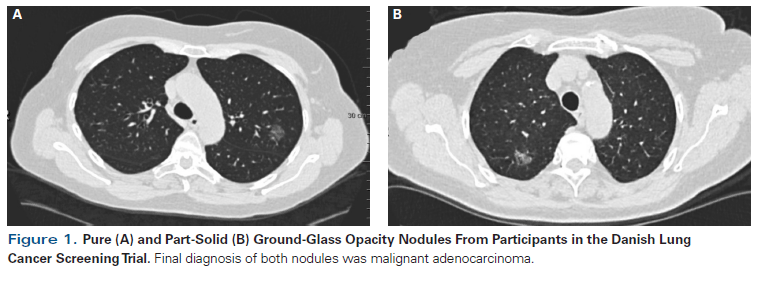
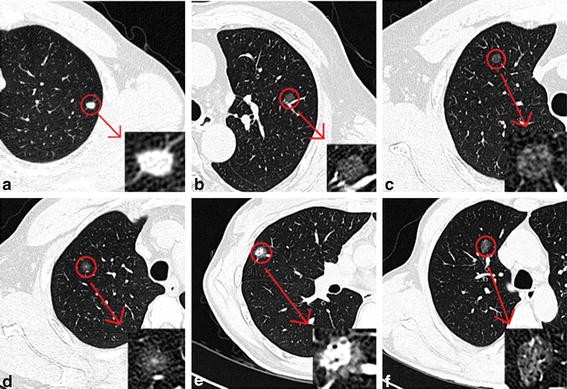
GGN ground-glass nodule. Initially she was thought to have bacterial or viral pneumonia given immunosuppression from chemotherapy or drug-related interstitial pneumonitis and was treated with antibiotics for three weeks. A ground-glass density nodule GGN is a circumscribed area of increased pulmonary attenuation with preservation of the bronchial and vascular margins.
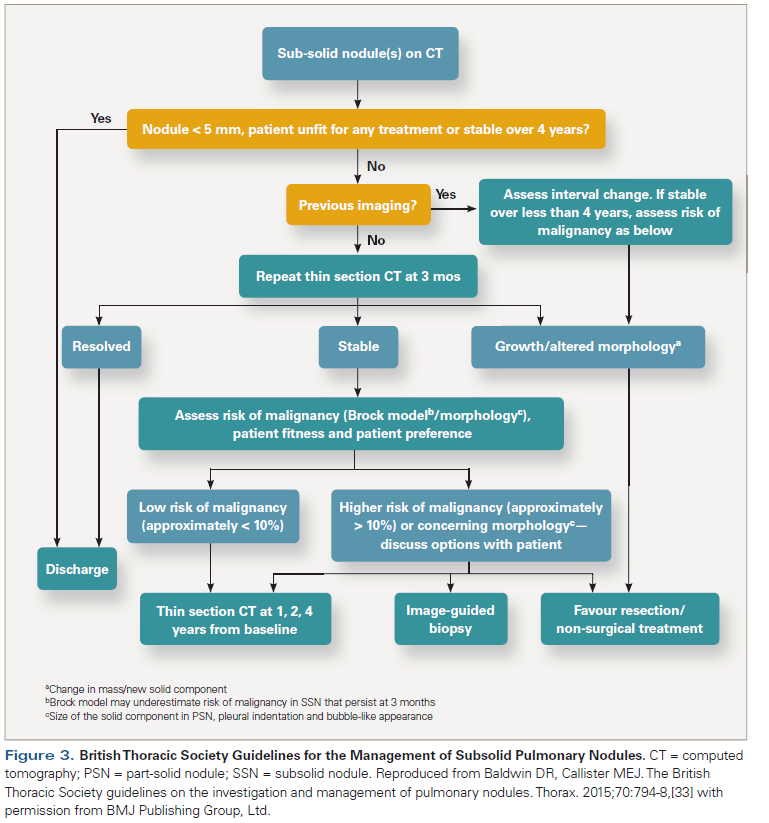
No role for transbronchial biopsy. Nodule and patient features can be used to estimate the probability of malignancy This probability can determine the next steps Long term follow up PET scan Surgery etc The PET scan has a very high NPV in the right scenario Benign features of nodules should allow conservative management. Repeat HRCT in 3 months 2.
2 nodules located at the outer one third of lung fields. Antibiotics may be prescribed for infections in the lungs and oxygen or bronchodilators are prescribed to help patients with silicosis breathe according to the American Lung Association. A GGN can be.
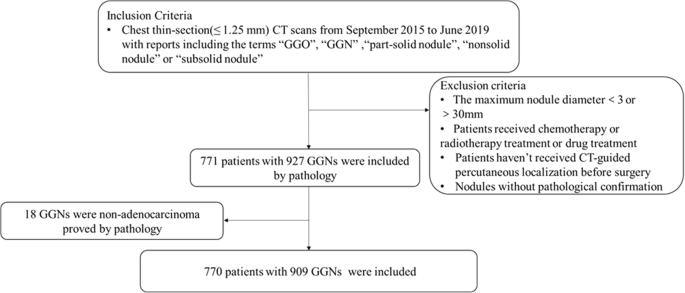
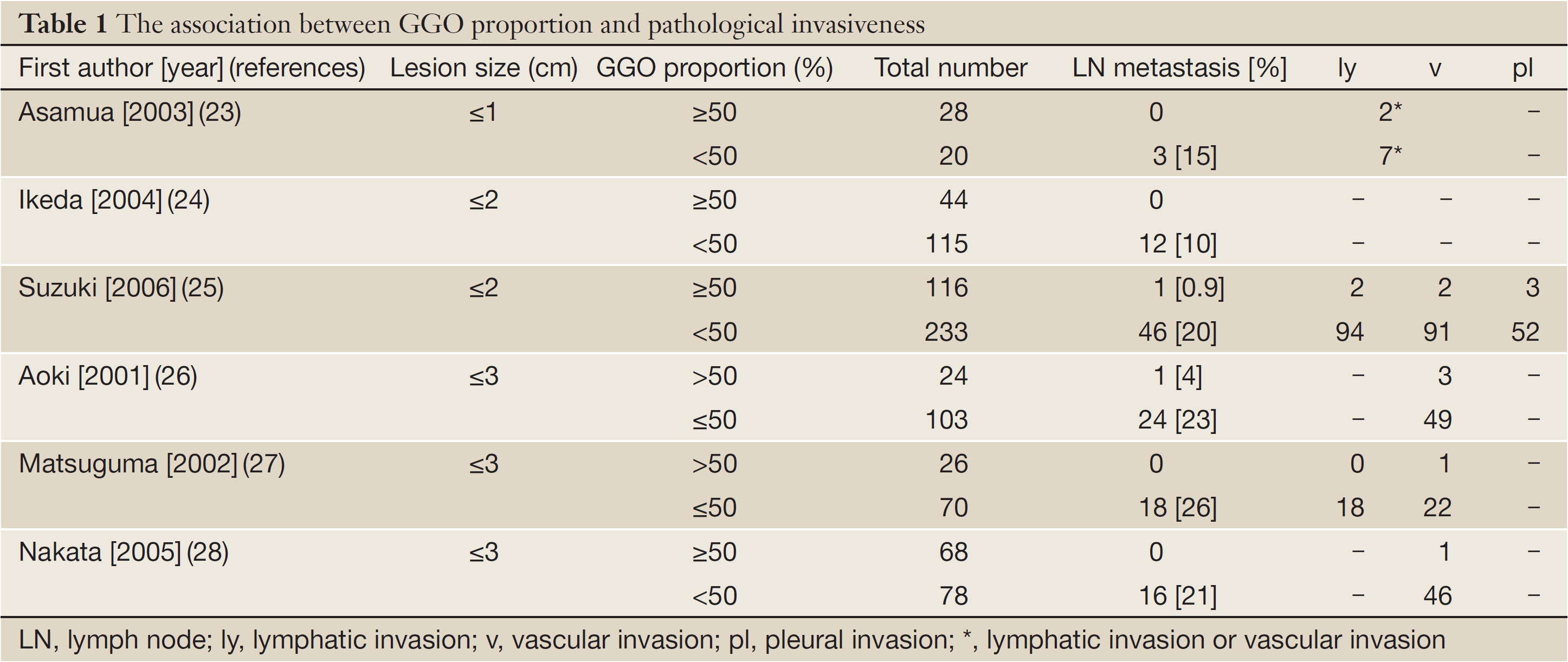
This means that clinical diagnosis and tumor invasiveness are often not available and surgical diagnosis is necessary. 19 linhas CT in 3 to 6 months. This discussion focuses on the management of.
If lesions persist annual HRCT for at least 3 years 3. However a recent research has shown that some ground-glass nodules may be treated with sublobar resections or non-surgical treatment. It is important to understand that some GGOs dont change their size for years while others grow their solid components over time.
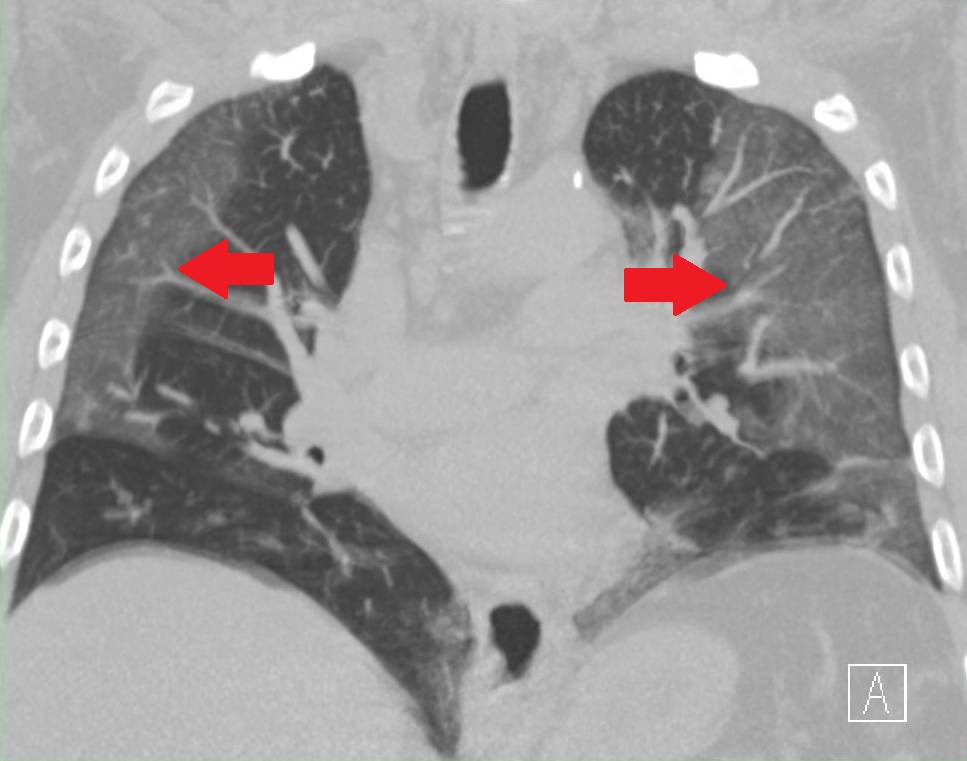
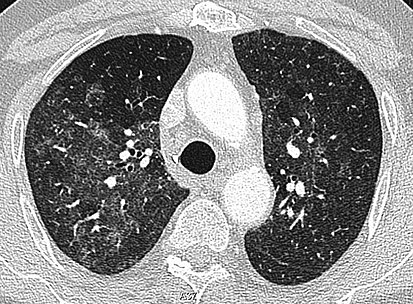
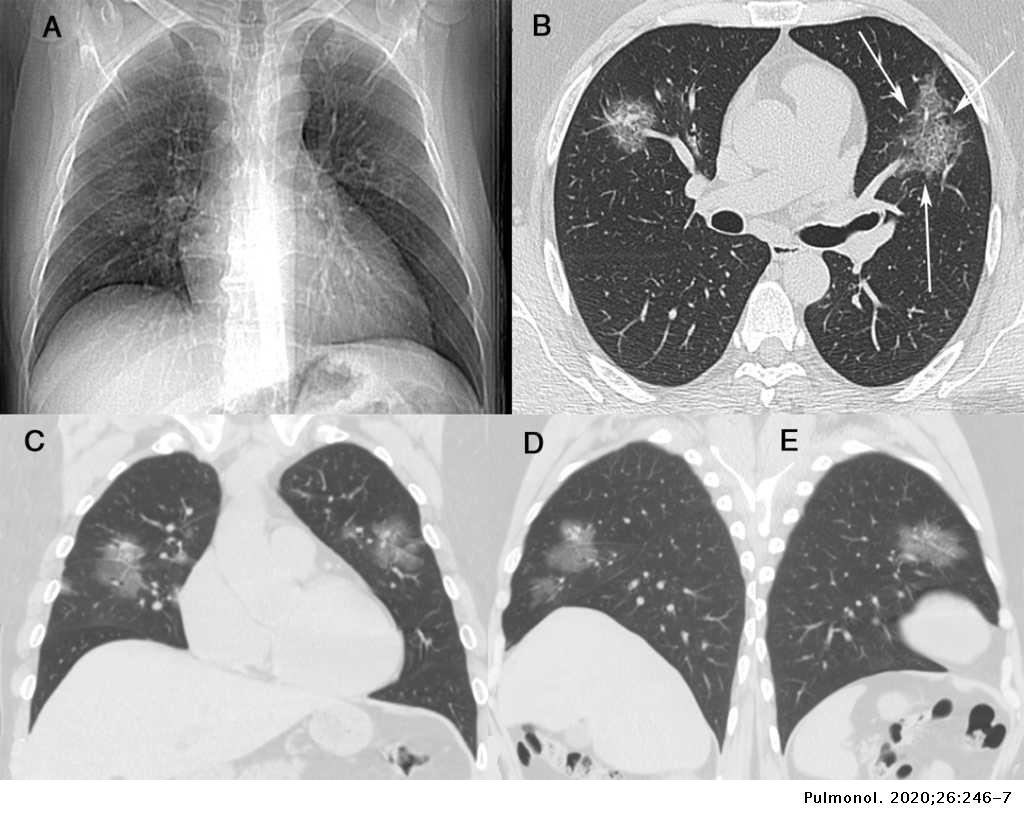
Treatment aims to slow the progression of the condition. Chest computed tomography showing patchy consolidations and ground glass opacity GGO in the subpleural area of both upper lobes and diffuse GGO bilaterally in the lower lobes.
If lesions persist annual HRCT for at least 3 years 3.
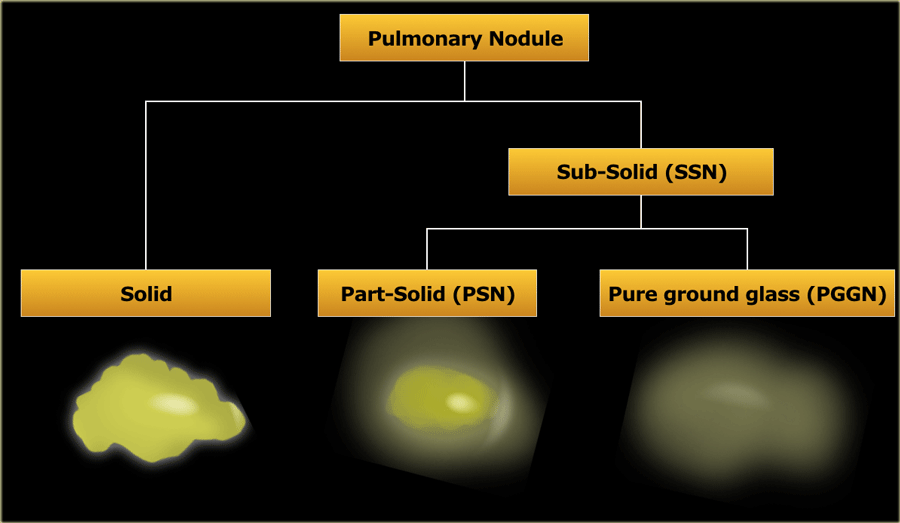
No role for transbronchial biopsy. Surgery stereotactic body radiation therapy SBRT and thermal tumor ablation including radiofrequency ablation microwave ablation and cryoablation. 2-3 weeks after the scan. GGO are usually described as either pure ground glass or part solid subsolid nodules. These findings may expand the treatment. Use consistent HRCT technique and measurement technique 4. Doctors may use supplemental oxygen anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressant drugs. Ground glass opacifications GGO are a subset of pulmonary nodules or masses with non-uniformity and less density than solid nodules. However a recent research has shown that some ground-glass nodules may be treated with sublobar resections or non-surgical treatment.
The surgical procedure is basically set as wedge resection but segmentectomy is allowed when the surgical margin is insufficient. Treatment aims to slow the progression of the condition. The results of JCOG 0804 were presented in ASCO 2017 47. These findings may expand the treatment. Second GGOs are difficult to detect at parenchymal palpation especially during video-assisted thoracoscopy surgery even if in the subpleural area. After 5 years the physician and patient can assume benignity and stability and stop following the nodule. For pure GGO nodules 5 mm in diameter a CT scan should be performed between 6 and 12 months in order to confirm persistence and then another CT scan should be performed every 2 years until the 5-year mark.















/multiple-lung-nodules-causes-and-diagnosis-2249390-v1-5c1ac161c9e77c000122ea44.png)




/lung-nodules-symptoms-causes-and-diagnosis-2249304_final11-5b44dd5cc9e77c003735e393.png)










Post a Comment for "Ground Glass Nodule Treatment"