Fetal Inflammatory Response Syndrome
Fetal inflammatory response syndrome. It is operationally defined as a fetal plasma IL-6 concentration above 11 ngL 61. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS is considered the counterpart of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome SIRS but similarities in their regulatory mechanisms are unclear. This study characterizes the fetal mRNA transcriptome of peripheral leukocytes to identify key biological processes and pathways involved in FIRS.
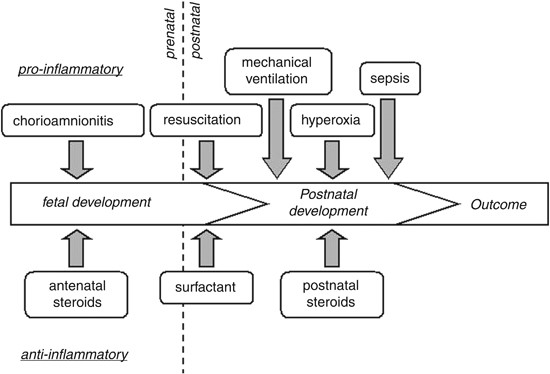
In this report we describe an infant of a SARS-CoV-2positive mother born prematurely with late-onset fever thrombocytopenia and elevated levels of inflammatory markers all of which are consistent with. Activates the maternal immune system as well as the fetus by creating an inflammatory environment. The inflammatory process can be localized to an organ eg the lung following fetal aspiration of amniotic fluid or become systemic when inflammatory.
Newborn affected by fetal inflammatory response syndrome 2019 - New Code 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code Code on Newborn Record P0270 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Amniocenteses and cordocenteses were performed in 157 patients with preterm labor and. Inflammation at the placenta has a bi-directional effect.
Fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS is an acute systemic inflammatory response to maternal intra-amniotic fluid infection such as. FIRS Fetal inflammatory response syndrome. This syndrome has been observed in fetuses with preterm labor with intact membranes preterm prelabor rupture of the membranes and also fetal viral infections such as cytomegalovirus.
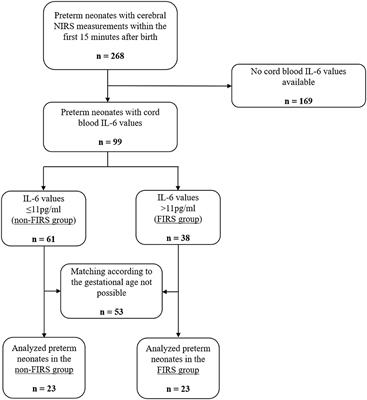
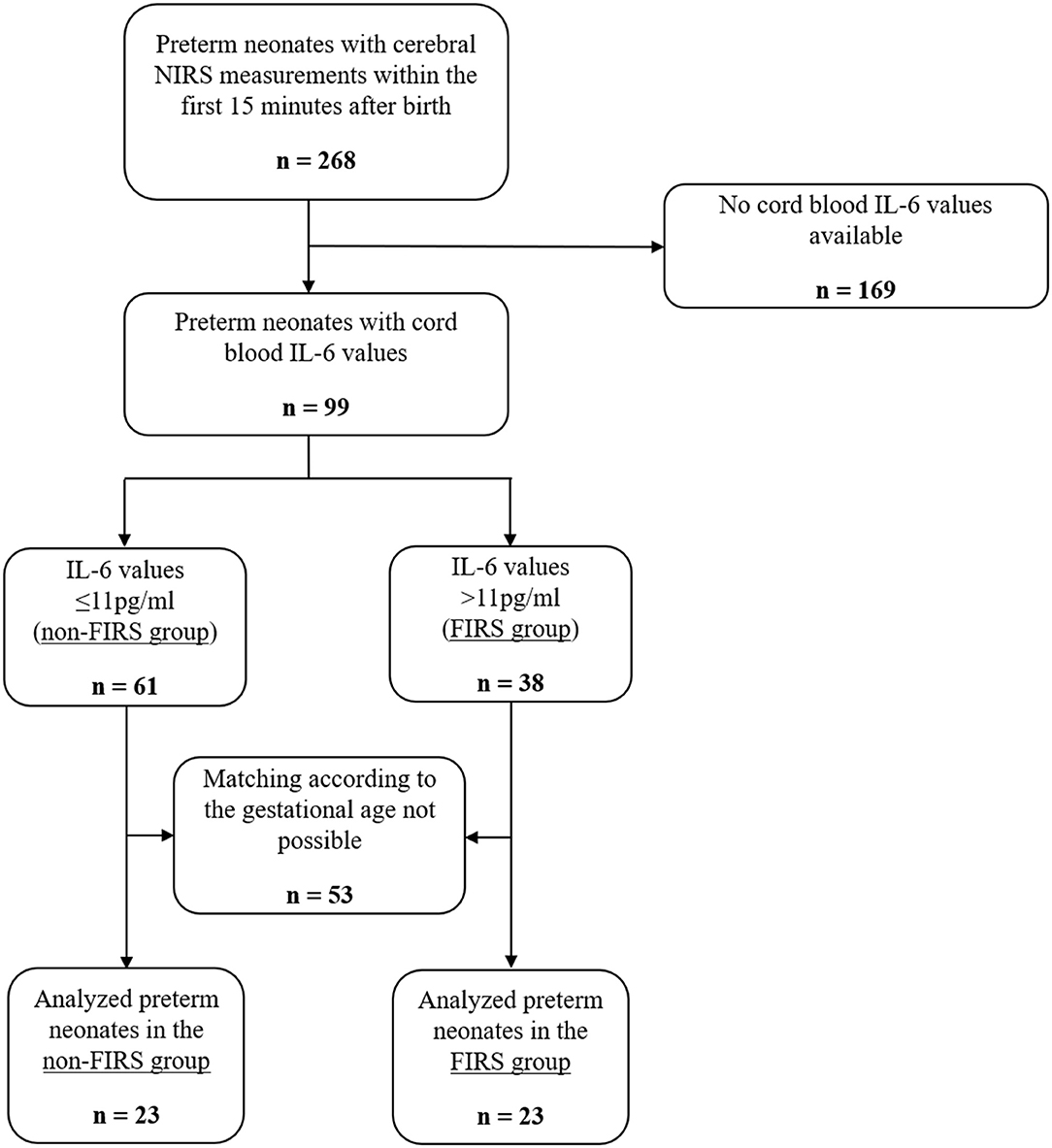
A systemic fetal inflammatory response as determined by an elevated fetal plasma interleukin-6 value is an independent risk factor for the occurrence of severe neonatal morbidity. Multiple factors then influence inflammatory responses during peripartum labor parturition and the immediate neonatal time periods clinically expressed as the fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS originally described in pregnancies complicated by spontaneous preterm labor and preterm prelabor rupture of membranes PROM is operationally defined as a fetal plasma interleukin-6 IL-6 concentration of 11 pgmL 12.
This syndrome has been observed in fetuses with preterm labor with intact membranes preterm prelabor rupture of the membranes and also fetal viral infections such as cytomegalovirus. Role of the placenta as a modulator of fetal and maternal responses. Temic inflammatory response as defined by an elevated plasma interleukin-6 concentration in fetuses with preterm labor or preterm premature rupture of membranes.
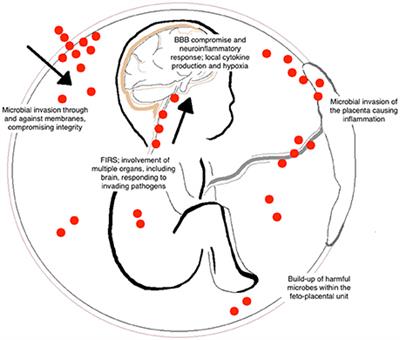
In this case report we aim to demonstrate the occurrence of a fetal inflammatory response syndrome associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection resulting in neonatal morbidity. The term fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS The human fetus can deploy an inflammatory response when exposed to microbial invasion with bacteria viruses 23 fungi 45 and protozoa or non-infection related stimuli.
The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS originally described in pregnancies complicated by spontaneous preterm labor and preterm prelabor rupture of membranes PROM is operationally defined as a fetal plasma interleukin-6 IL-6 concentration of 11 pgmL 12.
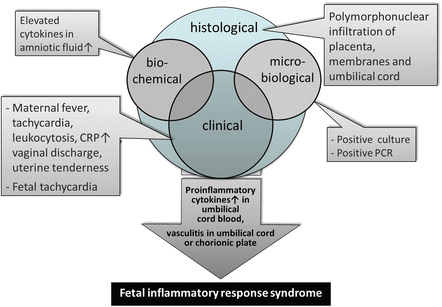
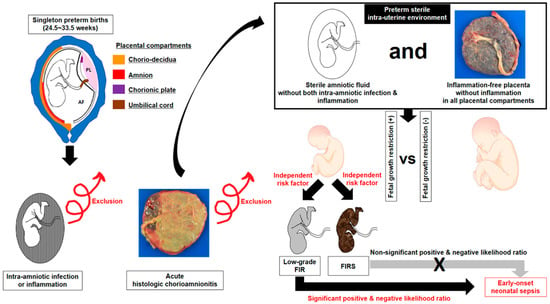
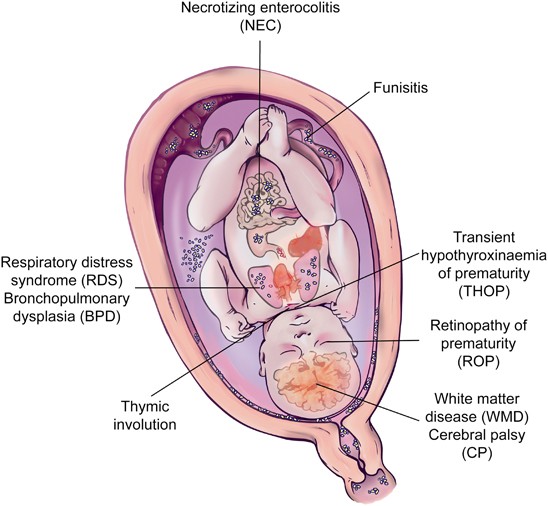
The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS is a subclinical condition originally described in fetuses presenting with preterm labor and intact membranes and preterm PROM. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS is a subclinical condition originally described in fetuses presenting with preterm labor and intact membranes and preterm PROM. Role of the placenta as a modulator of fetal and maternal responses. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS describes a state of extensive fetal multi organ involvement during chorioamnionitis and is associated with grave implications on perinatal outcome. A fetal plasma interleukin-6 cutoff value of 11 pgmL was used to define the presence of a systemic inflammatory response. Prognostic considerations require attention to trimester-specific influences that cumulatively contribute to this neonatal phenotype. Activates the maternal immune system as well as the fetus by creating an inflammatory environment. The inflammatory process can be localized to an organ eg the lung following fetal aspiration of amniotic fluid or become systemic when inflammatory. Fetal Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Cerebral Oxygenation During Immediate Postnatal Transition in Preterm Neonates Introduction.
The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS is a condition characterized by systemic inflammation and an elevation of fetal plasma interleukin-6. Inflammation at the placenta has a bi-directional effect. The prevalence of a fetal plasma interleukin-6 level. It is operationally defined as a fetal plasma IL-6 concentration above 11 ngL 61. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome FIRS describes a state of extensive fetal multi organ involvement during chorioamnionitis and is associated with grave implications on perinatal outcome. The syndrome has been linked to the preterm parturition syndrome and is associated with inflammationinfection processes in most of the fetal organs. FIRS Fetal inflammatory response syndrome.







































Post a Comment for "Fetal Inflammatory Response Syndrome"